Hello everyone, it’s been a while since I wrote a blog post .I got busy with my work . But now,I am back with a new blog post.
Last month I was working on a project where I need to setup the mysqld exporter for multiple mysql database. I tried to looking online for any documentation or blogs but I couldn’t find any blogs/documentation that explains how to setup the mysqld exporter for multiple hosts. After a lot googling and prompting(begging) with AI I was finally able to get it setup and running.
So I decided to write a blog on how to setup the mysqld exporter for multiple hosts for myself and for others who are looking for the solution.
Setting up the Database Link to heading
Before setting up the monitoring system we need something to monitor right .So we are going to setup couple of database servers using docker containers and in order to make the communication between our database and the monitoring system we will be leveraging the docker network.
First lets create the custom docker network where we will be running the database and the monitoring system.
docker network create mysql-network
Next spin up couple of database instance as the docker container using the below command
docker run -d --network mysql-network --name mysql1 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=super-secret-password -p 3306:3306 mysql
docker run -d --network mysql-network --name mysql2 -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=super-secret-password -p 3307:3306 mysql
Setting up the mysqld exporter Link to heading
Now that we have the database system up and running next step would be setting up the mysqld exporter. Similar to the database we will leverage the docker container to setup the mysqld exporter.
First let’s create the configuration file which will be used by the mysqld exporter to connect to the database server.
[client.client1]
host=mysql:3306
user=root
password=super-secret-password
[client.client2]
host=mysql2:3307
user=root
password=super-secret-password
Save the above configuration file as config.cnf in the current directory.
Now that we have the configuration file lets create the docker container for the mysqld exporter
docker run -d \
--network mysql-network \
--name mysqld-exporter \
-p 9104:9104 \
-v $(pwd)/config.cnf:/.my.cnf \
prom/mysqld-exporter
To verify that mysqld exporter is up and running the mysql exporter is able to connect to the database we can use the curl command to check the status of the exporter
curl "http://localhost:9104/probe?target=mysql1:3306&auth_module=client.client1"
curl "http://localhost:9104/probe?target=mysql2:3306&auth_module=client.client2"
Now that we are done with the setting up exposing the metrics the next step would be setting up the prometheus server to scrape the metrics that are being exported by the mysqld exporter.This is where I got stuck and I couldn’t find any documentation on how to setup the prometheus server to scrape the metrics that are being exported by the mysqld exporter.
Setting up the prometheus server Link to heading
First we have to create the prometheus.yml file with the below contents.
global:
scrape_interval: 15s
scrape_configs:
- job_name: mysql_multi_target
metrics_path: /probe
file_sd_configs:
- files:
- /etc/prometheus/targets.yml
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
- source_labels: [auth_module]
target_label: __param_auth_module
- target_label: __address__
replacement: mysqld-exporter:9104
Next we have to create the targets.yml file which has the list of the database servers that we want to monitor and along with the the authentication module as labels.
- labels:
auth_module: client.client1
targets:
- mysql1:3306
- labels:
auth_module: client.client2
targets:
- mysql2:3306
Let’s try to understand what is happening in the above configuration file.First we are telling the prometheus server to scrape the metrics from the endpoint(Basically this is the endpoint where the mysqld exporter is running)
- target_label: __address__
replacement: mysqld-exporter:9104
our endpoint looks like this this
http://mysqld-exporter:9104
The below line tells the exporter path to which we need to make the request to get the metrics
metrics_path: /probe
After adding the url path the endpoint looks like this
http://mysqld-exporter:9104/probe
The below lines tells the exporter to use the file_sd_configs to read the targets from the file targets.yml
file_sd_configs:
- files:
- /etc/prometheus/targets.yml
Our exporter exposes metrics for multiple targets so we have to tell the exporter to which target we want to make the request to get the metrics.In order to do that we are going to use the relabel features of the prometheus where its going to replace the target label with the target parameter for the request.
- source_labels: [__address__]
target_label: __param_target
So now our endpoint looks like this http://mysqld-exporter:9104?target=mysql1:3306
Finally we have to specify the auth_module which we have specified in the targets.yml file
- source_labels: [auth_module]
target_label: __param_auth_module
This will tell the exporter to use the auth_module label as the auth_module parameter for the request.
So now our endpoint looks like this http://mysqld-exporter:9104/target=mysql1:3306&auth_module=client.client1
Now that we have the configuration file lets create the docker container for the prometheus server
docker run -d \
--network mysql-network \
-p 9090:9090 \
-v $(pwd)/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml \
-v $(pwd)/targets.yml:/etc/prometheus/targets.yml \
prom/prometheus
Once you have the prometheus server up and running you can access the prometheus UI at http://localhost:9090 and you should be able to see the metrics that are being exported by the mysqld exporter by simply executing the following command
mysql_up
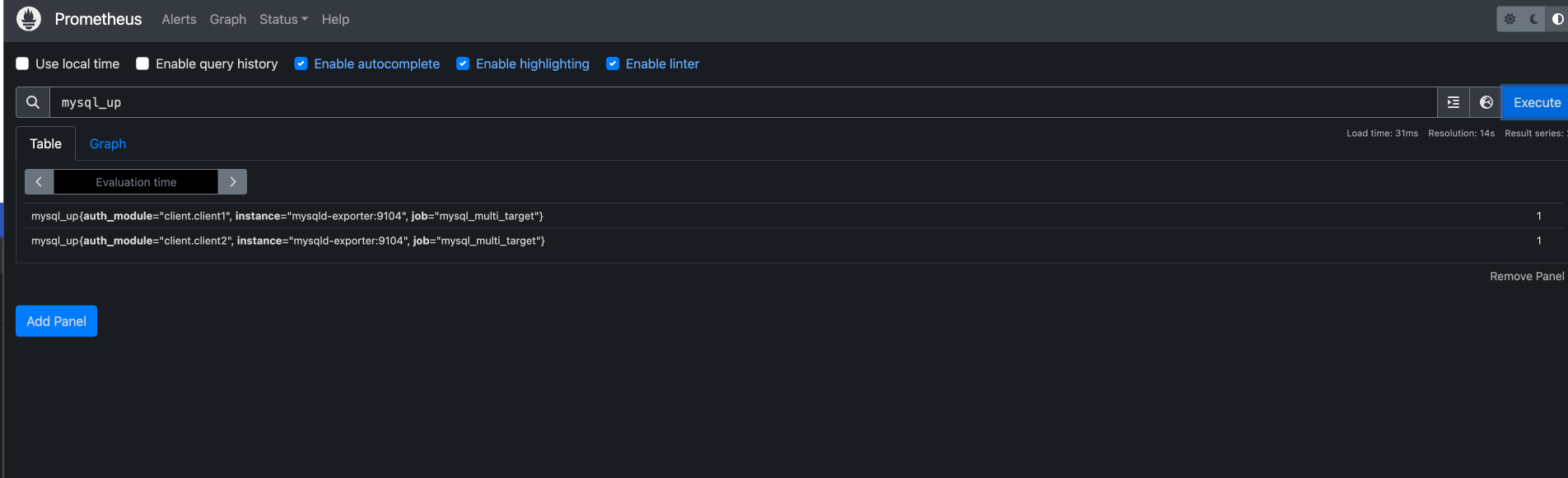
That it’s folks now we have successfully setup the prometheus server to scrape the metrics that are being exported by the mysqld exporter on multiple targets.I hope you found this blog post helpful.If you have any questions or suggestions please feel free to reach out to me. Thank you for reading.